cable bending tester
Understanding Cable Bending Testers Ensuring Quality and Reliability
In our ever-evolving technological landscape, the integrity and durability of cables are paramount. From power supply cables to data transfer conduits, the performance of these wires significantly influences the efficiency of electronic devices and systems. One essential tool in ensuring the longevity and functionality of cables is the cable bending tester.
A cable bending tester is an apparatus designed to assess the flexibility and durability of cables under various bending conditions. Cables, due to their inherent design and material construction, can exhibit different behaviors when subjected to bending, twisting, or compressive forces. When these cables are bent beyond their recommended parameters, they may suffer from mechanical failure, resulting in a loss of performance, power outages, or even damage to connected devices. The cable bending tester mitigates such risks by simulating real-world bending scenarios during quality assessment.
Typically, a cable bending tester employs a mechanical system that allows cables to be bent at predefined angles and radii. The equipment is engineered to replicate the types of movements cables experience in practical applications, such as being pulled through tight spaces, wrapped around objects, or moved in and out of machinery. By subjecting cables to a series of controlled bends, manufacturers can evaluate how specific models perform under stress and predict their lifespan in service.
cable bending tester
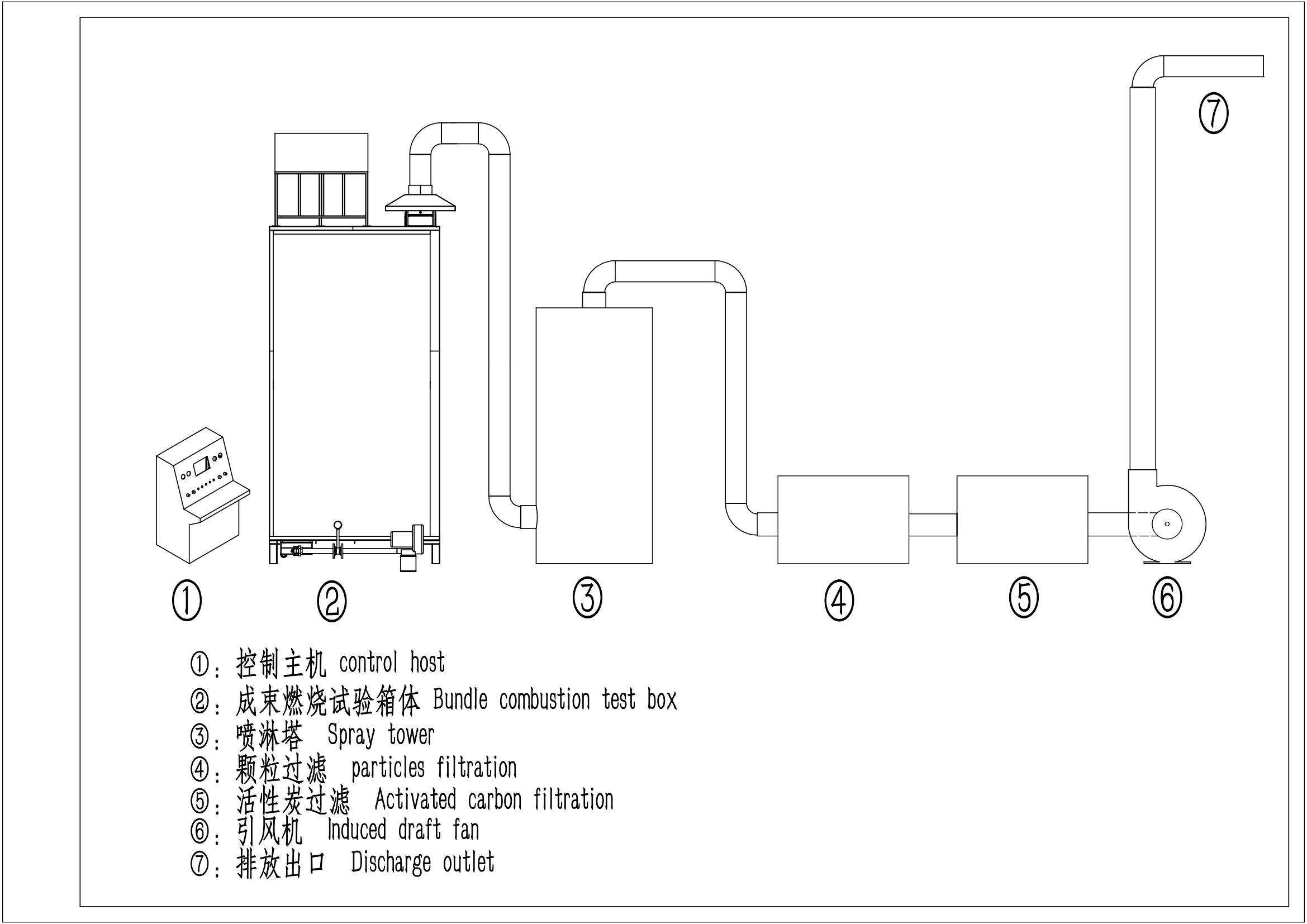
One of the key parameters measured during testing is the number of bending cycles a cable can endure before exhibiting significant wear or performance degradation. High-quality cables must withstand thousands of bends without showing visible damage or functional deficiencies. This continuous quality assurance not only guarantees a solid return on investment for manufacturers but also ensures reliability and satisfaction for end-users.
In addition to measuring bending resistance, cable bending testers can assess other properties such as electrical conductivity and insulation integrity. By monitoring these factors before and after bending tests, engineers can identify potential weaknesses in cable design and material composition. This comprehensive analysis serves to enhance product development, leading to the design of cables that are more resilient and effective in their intended applications.
Regulatory standards also play a crucial role in the implementation of cable bending testers in manufacturing facilities. Compliance with safety and performance regulations ensures that cables meet industry benchmarks for quality. Failing to adhere to these standards not only jeopardizes product reliability but may also expose manufacturers to potential legal liabilities. As a result, more manufacturers are integrating bending tests into their quality control processes to uphold high standards and accountability.
In conclusion, cable bending testers are an invaluable component of modern cable manufacturing and testing protocols. By accurately simulating real-world conditions and evaluating cable resilience, these devices ensure that cables remain functional and reliable throughout their intended lifespan. As technology continues to advance, the demand for robust and efficient cables will persist, making the role of bending testers even more critical in the quest for quality assurance. Investing in adequate testing machinery and adhering to industry standards can help manufacturers produce superior cables, ultimately benefiting both businesses and consumers alike.
-
Why the Conductor Resistance Constant Temperature Measurement Machine Redefines Precision
NewsJun.20,2025
-
Reliable Testing Starts Here: Why the High Insulation Resistance Measuring Instrument Is a Must-Have
NewsJun.20,2025
-
Flexible Cable Flexing Test Equipment: The Precision Standard for Cable Durability and Performance Testing
NewsJun.20,2025
-
Digital Measurement Projector: Precision Visualization for Modern Manufacturing
NewsJun.20,2025
-
Computer Control Electronic Tensile Tester: Precision and Power for the Modern Metal Industry
NewsJun.20,2025
-
Cable Spark Tester: Your Ultimate Insulation Assurance for Wire and Cable Testing
NewsJun.20,2025
 Copyright © 2025 Hebei Fangyuan Instrument & Equipment Co.,Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sitemap | Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2025 Hebei Fangyuan Instrument & Equipment Co.,Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Sitemap | Privacy Policy
